bisect.bisect_left(a, x)https://dynalist.io/d/RWIGNj7DLlzkBed-3ZqhuBg_#z=cbr2Mkrig9KhE6Lxfwhm31IS O(logn) greater than or equal to the targeted value. If all elements are less than x, returnlen(a)- l<=r or l < r
- ans1
- if you discard mid for the next iteration (i.e. l = mid+1 or r = mid-1) then use while (l <= r).
- if you keep mid for the next iteration (i.e. l = mid or r = mid) then use while (l < r)
- ans2
- if you are returning from inside the loop, use left <= right
- if you are reducing the search space, use left < right and finally return a[left]
- ans1
- l<=r or l < r
- template 1
can be determined by accessing a single index in the array.
- code, don’t use
(low+high)//2to avoid overflow.def bsearch(t, mylist): low, high = 0, len(mylist) - 1 while low <= high: mid = low + (high - low)//2 if mylist[mid] < t: low = mid + 1 elif mylist[mid] > t: high = mid - 1 else: return mid return -1remember mid + 1, -1, not mid itself
- code, don’t use
- template 2
accessing the current index and its immediate right neighbor’s index in the array.
- must be this way, r = mid - 1 and left = mid is wrong. If left, right, the mid is always left and left doesn’t change. Just remember to change left!
- code Explore - LeetCode
def binarySearch(nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: int """ if len(nums) == 0: return -1 left, right = 0, len(nums) while left < right: mid = (left + right) // 2 if nums[mid] == target: return mid elif nums[mid] < target: left = mid + 1 else: right = mid # Post-processing: # End Condition: left == right if left != len(nums) and nums[left] == target: return left return -1
- tempate 3
accessing the current index and its immediate left and right neighbor’s index in the array.
- code
def binarySearch(nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: int """ if len(nums) == 0: return -1 left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1 while left + 1 < right: mid = (left + right) // 2 if nums[mid] == target: return mid elif nums[mid] < target: left = mid else: right = mid # Post-processing: # End Condition: left + 1 == right if nums[left] == target: return left if nums[right] == target: return right return -1
300 Longest Increasing Subsequence
Given an unsorted array of integers, find the length of longest increasing subsequence. A subsequence is a sequence that can be derived from an array by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements. For example, [3,6,2,7] is a subsequence of the array [0,3,1,6,2,2,7].
Example:
Input: [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18] Output: 4 Explanation: The longest increasing subsequence is [2,3,7,101], therefore the length is 4.
class Solution:
def lengthOfLIS(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
L = [nums[0]]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] > L[-1]:
L.append(nums[i])
else:
# binary search to find the smallest number which is bigger than nums[i]
left = bisect.bisect_left(L, nums[i])
L[left] = nums[i]
# actuaclly 2,3,7,18
return len(L)
- code binary search
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
ArrayList<Integer> sub = new ArrayList<>();
sub.add(nums[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
int num = nums[i];
if (num > sub.get(sub.size() - 1)) {
sub.add(num);
} else {
int j = binarySearch(sub, num);
sub.set(j, num);
}
}
return sub.size();
}
private int binarySearch(ArrayList<Integer> sub, int num) {
int left = 0;
int right = sub.size();
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
while (left < right) {
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (sub.get(mid) == num) {
return mid;
}
if (sub.get(mid) < num) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return left;
}
}
410. Split Array Largest Sum
Split Array Largest Sum - LeetCode
Given an array nums which consists of non-negative integers and an integer m, you can split the array into m non-empty continuous subarrays. Write an algorithm to minimize the largest sum among these m subarrays.
Example 1: Input: nums = [7,2,5,10,8], m = 2 Output: 18 Explanation: There are four ways to split nums into two subarrays. The best way is to split it into [7,2,5] and [10,8], where the largest sum among the two subarrays is only 18. Example 2: Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5], m = 2 Output: 9
- code
class Solution {
private int minimumSubarraysRequired(int[] nums, int maxSumAllowed) {
int currentSum = 0;
int splitsRequired = 0;
for (int element : nums) {
// Add element only if the sum doesn't exceed maxSumAllowed
if (currentSum + element <= maxSumAllowed) {
currentSum += element;
} else {
// If the element addition makes sum more than maxSumAllowed
// Increment the splits required and reset sum
currentSum = element;
splitsRequired++;
}
}
// Return the number of subarrays, which is the number of splits + 1
return splitsRequired + 1;
}
public int splitArray(int[] nums, int m) {
// Define the left and right boundary of binary search
int left = Arrays.stream(nums).max().getAsInt();
int right = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();
int minimumLargestSplitSum = 0;
while (left <= right) {
// Find the mid value
int maxSumAllowed = left + (right - left) / 2;
// Find the minimum splits. If splitsRequired is less than
// or equal to m move towards left i.e., smaller values
if (minimumSubarraysRequired(nums, maxSumAllowed) <= m) {
right = maxSumAllowed - 1;
minimumLargestSplitSum = maxSumAllowed;
} else {
// Move towards right if splitsRequired is more than m
left = maxSumAllowed + 1;
}
}
return minimumLargestSplitSum;
}
}
- code #binarySearchAdvanced
class Solution:
def splitArray(self, nums: List[int], m: int) -> int:
def isTargetValid(target):
sub_ct = 0
cur_sum = 0
for v in nums:
if v + cur_sum <= target:
cur_sum += v
else:
cur_sum = v
sub_ct += 1
return sub_ct + 1
left, right = max(nums), sum(nums)
res = 0
while left <= right:
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if isTargetValid(mid) <= m: # need more sub groups, target value should be smaller
res = mid
right = mid - 1
else:
left = mid + 1
return res
- code
class Solution:
def splitArray(self, nums: List[int], m: int) -> int:
l, r = max(nums), sum(nums)
ans = r
while l <= r:
mid = l + (r-l) // 2
sub_sum = 0
ct = 1 # not 0
for v in nums:
if sub_sum + v > mid:
sub_sum = v # not 0
ct += 1
else:
sub_sum += v
if ct > m:
l = mid + 1
else:
ans = min(ans, mid)
r = mid - 1
return ans
1102. Path With Maximum Minimum Value
Given an m x n integer matrix grid, return __the maximum score of a path starting at (0, 0) and ending at __(m - 1, n - 1) moving in the 4 cardinal directions. The score of a path is the minimum value in that path.
For example, the score of the path 8 → 4 → 5 → 9 is 4.
Example 1:
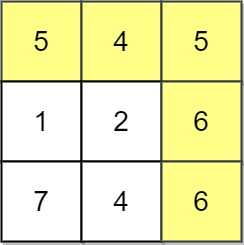 Input: grid = [[5,4,5],[1,2,6],[7,4,6]] Output: 4 Explanation: The path with the maximum score is highlighted in yellow.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[5,4,5],[1,2,6],[7,4,6]] Output: 4 Explanation: The path with the maximum score is highlighted in yellow.
Example 2:
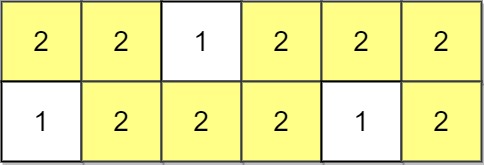 Input: grid = [[2,2,1,2,2,2],[1,2,2,2,1,2]] Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[2,2,1,2,2,2],[1,2,2,2,1,2]] Output: 2
Example 3:
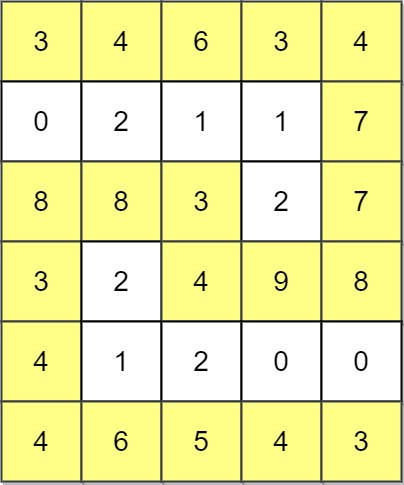 Input: grid = [[3,4,6,3,4],[0,2,1,1,7],[8,8,3,2,7],[3,2,4,9,8],[4,1,2,0,0],[4,6,5,4,3]] Output: 3
Input: grid = [[3,4,6,3,4],[0,2,1,1,7],[8,8,3,2,7],[3,2,4,9,8],[4,1,2,0,0],[4,6,5,4,3]] Output: 3
Constraints:
m == grid.length
n == grid[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 100
0 <= grid[i][j] <= 109
- code #binarySearchAdvanced
class Solution:
def maximumMinimumPath(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
directions = [(-1, 0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1)]
def dfs(i, j, mini, visited):
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1:
return True
visited[i][j] = True
for dx, dy in directions:
nx, ny = i + dx, j + dy
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and not visited[nx][ny]:
if grid[nx][ny] >= mini:
if dfs(nx, ny, mini, visited): return True
return False
res = 0
start, end = 0, min(grid[0][0], grid[-1][-1]) + 1 # left open, right closed so plus one
while start < end:
mid = (start + end) // 2
visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
if dfs(0, 0, mid, visited):
start = mid + 1 # current is working, move to one step right
else:
end = mid
return end - 1 # or start - 1
- code #unionfind #unionFindTrickToFlat flat two dimensions to one list
curPosition = curRow * len(grid[0]) + curCol
class Solution:
def maximumMinimumPath(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# Find the root of x.
def find(x):
if x != root[x]:
root[x] = find(root[x])
return root[x]
# Union the roots of x and y.
def union(x, y):
root_x = find(x)
root_y = find(y)
if root_x != root_y:
if rank[root_x] > rank[root_y]:
root[root_y] = root_x
elif rank[root_x] < rank[root_y]:
root[root_x] = root_y
else:
root[root_y] = root_x
rank[root_x] += 1
R = len(grid)
C = len(grid[0])
# 4 directions to a cell's possible neighbors.
dirs = [(1, 0), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (0, -1)]
# Intialize the rank of all the cells.
rank = [1] * (R * C)
# Intialize the root of all the cells.
root = list(range(R * C))
# Mark all the cells as false (unvisited).
visited = [[False] * C for _ in range(R)]
# Sort all the cells by values from large to small.
vals = [(row, col) for row in range(R) for col in range(C)]
vals.sort(key = lambda x: grid[x[0]][x[1]], reverse = True)
# Iteration over the sorted cells.
for cur_row, cur_col in vals:
cur_pos = cur_row * C + cur_col
# Mark the current cell as true (visited).
visited[cur_row][cur_col] = True
for d_row, d_col in dirs:
new_row = cur_row + d_row
new_col = cur_col + d_col
new_pos = new_row * C + new_col
# Check if the current cell has any unvisited neighbors with value larger
# than or equal to val.
if 0 <= new_row < R and 0 <= new_col < C and visited[new_row][new_col]:
# If so, we connect the current cell with this neighbor.
union(cur_pos, new_pos)
# Check if the top-left cell is connected with the bottom-right cell.
if find(0) == find(R * C - 1):
# If so, return the value of the current cell.
return grid[cur_row][cur_col]
return -1
- code #priorityQueue
class Solution:
def maximumMinimumPath(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
R = len(grid)
C = len(grid[0])
# 4 directions to a cell's possible neighbors.
dirs = [(1, 0), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (0, -1)]
heap = []
ans = grid[0][0]
# Initalize the status of all the cells as 0 (unvisited).
visited = [[False] * C for _ in range(R)]
# Put the top-left cell to the priority queue and mark it as True (visited).
# Notice that we save the negative number of cell's value, thus we can always
# pop out the cell with the maximum value using a min-heap data structure.
heapq.heappush(heap, (-grid[0][0], 0, 0))
visited[0][0] = True
# While the priority queue is not empty.
while heap:
# Pop the cell with the largest value.
cur_val, cur_row, cur_col = heapq.heappop(heap)
# Update the minimum value we have visited so far.
ans = min(ans, grid[cur_row][cur_col])
# If we reach the bottom-right cell, stop the iteration.
if cur_row == R - 1 and cur_col == C - 1:
break
for d_row, d_col in dirs:
new_row = cur_row + d_row
new_col = cur_col + d_col
# Check if the current cell has any unvisited neighbors.
if 0 <= new_row < R and 0 <= new_col < C and not visited[new_row][new_col]:
# If so, we put this neighbor to the priority queue
# and mark it as True (visited).
heapq.heappush(heap, (-grid[new_row][new_col], new_row, new_col))
visited[new_row][new_col] = True
# Return the minimum value we have seen, which is the value of this path.
return ans
- code #binarySearchAdvanced
class Solution:
def maximumMinimumPath(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
directions = [(-1, 0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1)]
def dfs(i, j, mini, visited):
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1:
return True
visited[i][j] = True
for dx, dy in directions:
nx, ny = i + dx, j + dy
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and not visited[nx][ny]:
if grid[nx][ny] >= mini:
if dfs(nx, ny, mini, visited): return True
return False
res = 0
start, end = 0, min(grid[0][0], grid[-1][-1]) + 1 # left open, right closed so plus one
while start < end:
mid = (start + end) // 2
visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
if dfs(0, 0, mid, visited):
start = mid + 1 # current is working, move to one step right
else:
end = mid
return end - 1 # or start - 1
- code TLE with backtracking trying to check all paths
class Solution:
def maximumMinimumPath(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
self.res = 0
directions = [(-1, 0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1)]
def backtracking(i, j, mini, visited):
# print(visited)
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1:
self.res = max(self.res, mini)
return
for dx, dy in directions:
nx, ny = i + dx, j + dy
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and (nx, ny) not in visited:
visited.add((nx, ny))
oldmini = mini
backtracking(nx, ny, min(mini, grid[nx][ny]), visited)
visited.remove((nx, ny))
mini = oldmini
visited = set()
visited.add((0, 0))
backtracking(0, 0, grid[0][0], visited)
return self.res
- code java bs
class Solution {
private int R, C;
// 4 directions to a cell's possible neighbors.
private int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
public int maximumMinimumPath(int[][] grid) {
R = grid.length;
C = grid[0].length;
int left = 0, right = Math.min(grid[0][0], grid[R - 1][C - 1]);
while (left < right) {
// Get the middle value between left and right boundaries.
int middle = (right + left + 1) / 2;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[R][C];
// Check if we can find a path with value = middle, and cut
// the search space by half.
if (pathExists(grid, middle, visited, 0, 0)) {
left = middle;
} else {
right = middle - 1;
}
}
// Once the left and right boundaries coincide, we find the target value,
// that is, the maximum value of a path.
return left;
}
// Check if we can find a path of value = val.
private boolean pathExists(int[][] grid, int val, boolean[][] visited, int curRow, int curCol) {
// If we reach the bottom-right cell, return true.
if (curRow == R - 1 && curCol == C - 1) return true;
// Mark the current cell as visited.
visited[curRow][curCol] = true;
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int newRow = curRow + dir[0];
int newCol = curCol + dir[1];
// Check if the current cell has any unvisited neighbors with value larger
// than or equal to val.
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < R && newCol >= 0 && newCol < C
&& !visited[newRow][newCol] && grid[newRow][newCol] >= val) {
// If so, we continue search on this neighbor.
if (pathExists(grid, val, visited, newRow, newCol))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
1631. Path With Minimum Effort
You are a hiker preparing for an upcoming hike. You are given heights, a 2D array of size rows x columns, where heights[row][col] represents the height of cell (row, col). You are situated in the top-left cell, (0, 0), and you hope to travel to the bottom-right cell, (rows-1, columns-1) (i.e., 0-indexed). You can move up, down, left, or right, and you wish to find a route that requires the minimum effort. A route’s effort is the maximum absolute difference in heights between two consecutive cells of the route. Return the minimum effort required to travel from the top-left cell to the bottom-right cell.
Example 1:
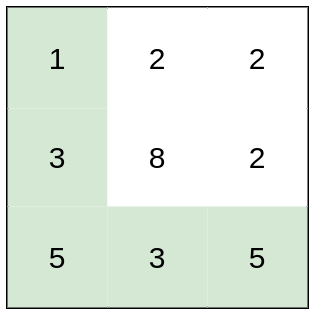 Input: heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] Output: 2 Explanation: The route of [1,3,5,3,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 2 in consecutive cells. This is better than the route of [1,2,2,2,5], where the maximum absolute difference is 3.
Example 2:
Input: heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] Output: 2 Explanation: The route of [1,3,5,3,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 2 in consecutive cells. This is better than the route of [1,2,2,2,5], where the maximum absolute difference is 3.
Example 2:
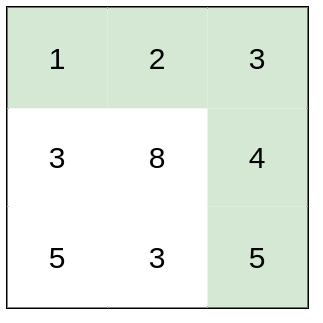 Input: heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] Output: 1 Explanation: The route of [1,2,3,4,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 1 in consecutive cells, which is better than route [1,3,5,3,5].
Example 3:
Input: heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] Output: 1 Explanation: The route of [1,2,3,4,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 1 in consecutive cells, which is better than route [1,3,5,3,5].
Example 3:
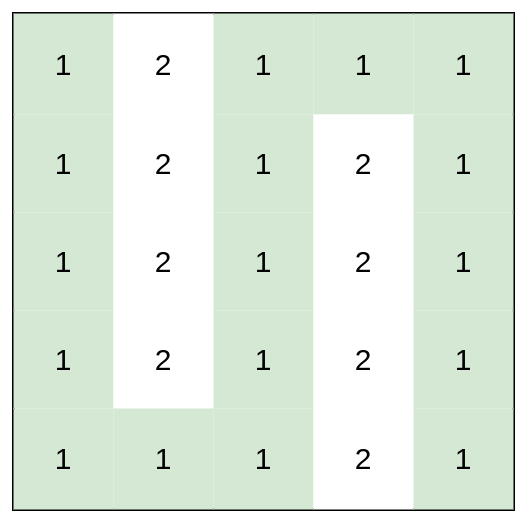 Input: heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] Output: 0 Explanation: This route does not require any effort.
Input: heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] Output: 0 Explanation: This route does not require any effort.
Constraints:
rows == heights.length
columns == heights[i].length
1 <= rows, columns <= 100
1 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
- code BFS + #binarySearchAdvanced
class Solution:
def minimumEffortPath(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dirs = [(-1, 0),(1, 0),(0, 1),(0, -1)]
rowL, colL = len(heights), len(heights[0])
def isPathValid(maxDiff):
q = deque([(0, 0)])
visited = set((0, 0))
while q:
curi, curj = q.popleft()
if curi == rowL - 1 and curj == colL - 1: return True
for di, dj in dirs:
ni, nj = curi + di, curj + dj
if 0 <= ni < rowL and 0 <= nj < colL and (ni, nj) not in visited and abs(heights[ni][nj] - heights[curi][curj]) <= maxDiff:
q.append((ni, nj))
visited.add((ni, nj))
return False
left, right = 0, 10 ** 6
while left < right:
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if isPathValid(mid):
right = mid
else:
left = mid + 1
return right
- code java
class Solution {
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int left = 0;
int right = 1000000;
int result = right;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (canReachDestinaton(heights, mid)) {
result = Math.min(result, mid);
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return result;
}
int[][] directions = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
// use bfs to check if we can reach destination with max absolute difference k
boolean canReachDestinaton(int[][] heights, int k) {
int row = heights.length;
int col = heights[0].length;
Deque<Cell> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[heights.length][heights[0].length];
queue.addLast(new Cell(0, 0));
visited[0][0] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Cell curr = queue.removeFirst();
if(curr.x == row - 1 && curr.y == col - 1) {
return true;
}
for (int[] direction : directions) {
int adjacentX = curr.x + direction[0];
int adjacentY = curr.y + direction[1];
if (isValidCell(adjacentX, adjacentY, row, col) && !visited[adjacentX][adjacentY]) {
int currentDifference = Math.abs(heights[adjacentX][adjacentY] - heights[curr.x][curr.y]);
if (currentDifference <= k) {
visited[adjacentX][adjacentY] = true;
queue.addLast(new Cell(adjacentX, adjacentY));
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
boolean isValidCell(int x, int y, int row, int col) {
return x >= 0 && x <= row - 1 && y >= 0 && y <= col - 1;
}
}
class Cell {
int x;
int y;
Cell(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
- code DFS + binary search
class Solution:
def minimumEffortPath(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> int:
row = len(heights)
col = len(heights[0])
def canReachDestinaton(x, y, mid):
if x == row-1 and y == col-1:
return True
visited[x][y] = True
for dx, dy in [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]]:
adjacent_x = x + dx
adjacent_y = y + dy
if 0 <= adjacent_x < row and 0 <= adjacent_y < col and not visited[
adjacent_x][adjacent_y]:
current_difference = abs(
heights[adjacent_x][adjacent_y]-heights[x][y])
if current_difference <= mid:
visited[adjacent_x][adjacent_y] = True
if canReachDestinaton(adjacent_x, adjacent_y, mid):
return True
left = 0
right = 10000000
while left < right:
mid = (left + right)//2
visited = [[False]*col for _ in range(row)]
if canReachDestinaton(0, 0, mid):
right = mid
else:
left = mid + 1
return left
The real reason why the binary search approach works with BFS or DFS is that by defining a diff limit, the search space dramatically decreased, because we don’t need BFS/DFS to exhaust all the paths to the target anymore, we just need to find ONE path that satisfy the diff limit. Thus, if we find ourself at a Cell that satisfies a diff limit, we don’t care about other paths that get to this Cell anymore, that’s why we can use “visited” to eliminate paths exploration. Without a diff limit, we can no longer use this naive “visited” way of tracking and the search space becomes 3^(M*N) as we’d have to exhaust all the paths to find the one with min diff. -billmaxwell on leetcode https://leetcode.com/problems/path-with-minimum-effort/solution/977158
- code
class Solution {
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int left = 0;
int right = 1000000;
int result = right;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (dfsUtil(heights, mid)) {
result = Math.min(result, mid);
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return result;
}
int[][] directions = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
boolean dfsUtil(int[][] heights, int mid) {
int row = heights.length;
int col = heights[0].length;
boolean visited[][] = new boolean[row][col];
return canReachDestinaton(0, 0, heights, visited, row, col, mid);
}
boolean canReachDestinaton(int x, int y, int[][] heights,
boolean[][] visited, int row, int col, int mid) {
if (x == row - 1 && y == col - 1) {
return true;
}
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int[] direction : directions) {
int adjacentX = x + direction[0];
int adjacentY = y + direction[1];
if (isValidCell(adjacentX, adjacentY, row, col) && !visited[adjacentX][adjacentY]) {
int currentDifference = Math.abs(heights[adjacentX][adjacentY] - heights[x][y]);
if (currentDifference <= mid) {
if (canReachDestinaton(adjacentX, adjacentY, heights, visited, row, col, mid))
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
boolean isValidCell(int x, int y, int row, int col) {
return x >= 0 && x <= row - 1 && y >= 0 && y <= col - 1;
}
}