Maximum Width of Binary Tree - LeetCode
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum width of the given tree. The maximum width of a tree is the maximum width among all levels. The width of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes are also counted into the length calculation. It is guaranteed that the answer will in the range of 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
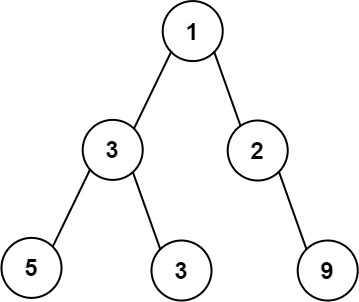 Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] Output: 4 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the third level with the length 4 (5,3,null,9).
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] Output: 4 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the third level with the length 4 (5,3,null,9).
Example 2:
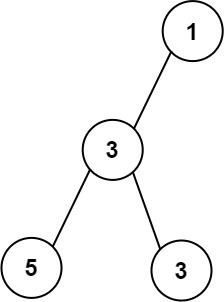 Input: root = [1,3,null,5,3] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the third level with the length 2 (5,3).
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,3,null,5,3] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the third level with the length 2 (5,3).
Example 3:
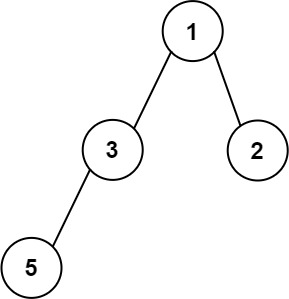 Input: root = [1,3,2,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the second level with the length 2 (3,2).
Input: root = [1,3,2,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the second level with the length 2 (3,2).
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 3000].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
- code bfs
class Solution:
def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
q = deque([(root, 0)])
maxWidth = 0
while q:
headCol = q[0][1]
for _ in range(len(q)):
curNode, curCol = q.popleft()
if curNode.left:
q.append((curNode.left, 2 * curCol))
if curNode.right:
q.append((curNode.right, 2 * curCol + 1))
maxWidth = max(maxWidth, curCol - headCol + 1)
return maxWidth
- code dfs the nodes at the same level do get visited from left to right.
class Solution:
def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
# table contains the first col_index for each level
first_col_index_table = {}
self.max_width = 0
def DFS(node, depth, col_index):
if not node: return
# if the entry is empty, set the value
if depth not in first_col_index_table:
first_col_index_table[depth] = col_index
self.max_width = max(self.max_width, col_index - first_col_index_table[depth] + 1)
# Preorder DFS, with the priority on the left child
DFS(node.left, depth+1, 2*col_index)
DFS(node.right, depth+1, 2*col_index + 1)
DFS(root, 0, 0)
return self.max_width