Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of every tree node’s tilt. The tilt of a tree node is the absolute difference between the sum of all left subtree node values and all right subtree nsode values. If a node does not have a left child, then the sum of the left subtree node values is treated as 0. The rule is similar if there the node does not have a right child.
Example 1:
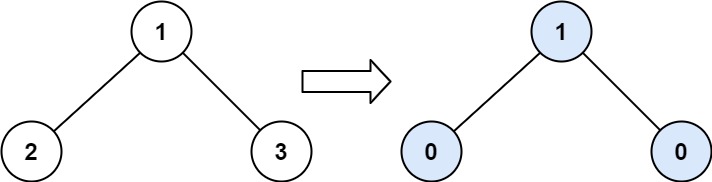
Input: root = [1,2,3] Output: 1 Explanation: Tilt of node 2 : |0-0| = 0 (no children) Tilt of node 3 : |0-0| = 0 (no children) Tilt of node 1 : |2-3| = 1 (left subtree is just left child, so sum is 2; right subtree is just right child, so sum is 3) Sum of every tilt : 0 + 0 + 1 = 1
- code
class Solution:
def findTilt(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def helper(root):
if not root:
return (0,0)
left_tilt, left_sum = helper(root.left)
right_tilt, right_sum = helper(root.right)
return (abs(right_sum - left_sum) + left_tilt + right_tilt, left_sum + right_sum + root.val)
return helper(root)[0]