Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order. A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
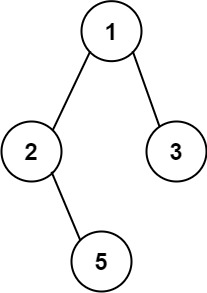 Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5] Output: [“1->2->5”,“1->3”]
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5] Output: [“1->2->5”,“1->3”]
Example 2: Input: root = [1] Output: [“1”]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
- code
class Solution:
def binaryTreePaths(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[str]:
def dfs(node, path):
if node:
if not node.left and not node.right:
res.append("->".join(path + [str(node.val)]))
dfs(node.left, path + [str(node.val)])
dfs(node.right, path + [str(node.val)])
res = []
dfs(root, [])
return res
- code
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<String> paths = new LinkedList();
if (root == null)
return paths;
LinkedList<TreeNode> node_stack = new LinkedList();
LinkedList<String> path_stack = new LinkedList();
node_stack.add(root);
path_stack.add(Integer.toString(root.val));
TreeNode node;
String path;
while ( !node_stack.isEmpty() ) {
node = node_stack.pollLast();
path = path_stack.pollLast();
if ((node.left == null) && (node.right == null))
paths.add(path);
if (node.left != null) {
node_stack.add(node.left);
path_stack.add(path + "->" + Integer.toString(node.left.val));
}
if (node.right != null) {
node_stack.add(node.right);
path_stack.add(path + "->" + Integer.toString(node.right.val));
}
}
return paths;
}
}