Insertion Sort List - LeetCode Given the head of a singly linked list, sort the list using insertion sort, and return the sorted list’s head. The steps of the insertion sort algorithm:
Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition and growing a sorted output list. At each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list and inserts it there. It repeats until no input elements remain.The following is a graphical example of the insertion sort algorithm. The partially sorted list (black) initially contains only the first element in the list. One element (red) is removed from the input data and inserted in-place into the sorted list with each iteration.

Example 1:
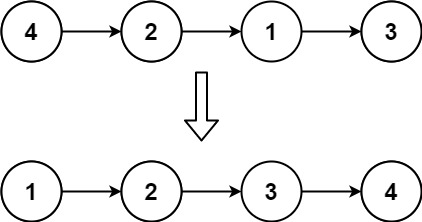 Input: head = [4,2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3,4]
Input: head = [4,2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3,4]
- code
class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dum = new ListNode();
while (head != null){
ListNode to_insert = head;
head = head.next;
ListNode prev = dum;
while (prev.next != null && prev.next.val < to_insert.val){
prev = prev.next;
}
to_insert.next = prev.next;
prev.next = to_insert;
}
return dum.next;
}
}
- code
class Solution:
def insertionSortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
self.res = None
def insertion_sort(node): # be care of node.next may exist
# node becomes new head
if not self.res or node.val <= self.res.val:
node.next = self.res
self.res = node
else:
# find position to insert
dumb = ListNode(0, self.res)
while dumb.next and node.val > dumb.next.val:
dumb = dumb.next
# insert
node.next = dumb.next
dumb.next = node
while head:
to_ins = head
head = head.next
insertion_sort(to_ins)
return self.res
- code
class Solution:
def insertionSortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode() # dummy.next will be ans
while head:
to_ins = head
head = head.next
prev = dummy # find postion to insert
while prev.next and prev.next.val < to_ins.val:
prev = prev.next
# insert
to_ins.next = prev.next
prev.next = to_ins
return dummy.next