https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a “linked list”:
The "linked list" should use the same TreeNode class where the right child pointer points to the next node in the list and the left child pointer is always null.
The "linked list" should be in the same order as a [pre-order traversal](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal#Pre-order,_NLR) of the binary tree.
Example 1:
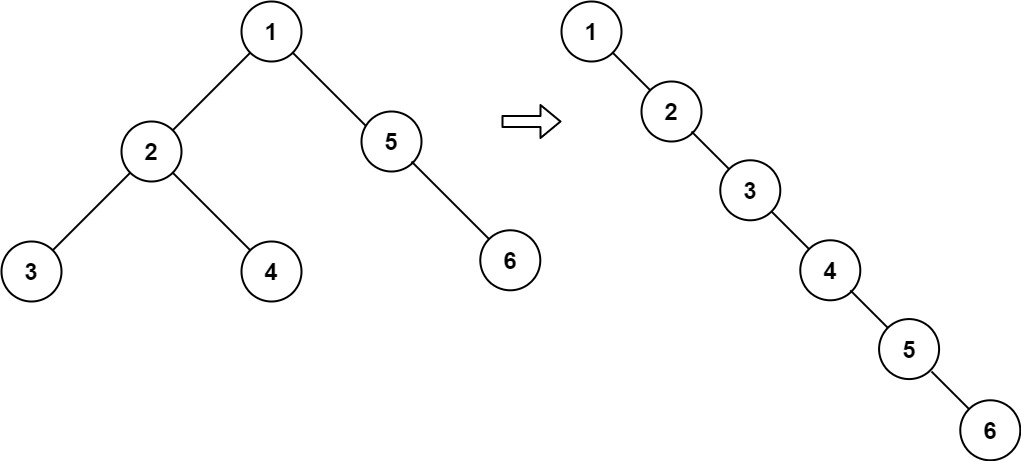 Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 2000].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
- code
class Solution {
List<TreeNode> res;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
pre(root);
for (int i = 0; i < res.size() - 1; i++){
res.get(i).right = res.get(i+1);
res.get(i).left = null;
}
}
public void pre(TreeNode node){
if (node == null) return;
res.add(node);
pre(node.left);
pre(node.right);
}
}
- code
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
// Handle the null scenario
if (root == null) {
return;
}
TreeNode node = root;
while (node != null) {
// If the node has a left child
if (node.left != null) {
// Find the rightmost node
TreeNode rightmost = node.left;
while (rightmost.right != null) {
rightmost = rightmost.right;
}
// rewire the connections
rightmost.right = node.right;
node.right = node.left;
node.left = null;
}
// move on to the right side of the tree
node = node.right;
}
}
}