Shortest Path in Binary Matrix - LeetCode
Given an n x n binary matrix grid, return the length of the shortest clear path in the matrix. If there is no clear path, return -1. A clear path in a binary matrix is a path from the top-left cell (i.e., (0, 0)) to the bottom-right cell (i.e., (n - 1, n - 1)) such that:
All the visited cells of the path are 0. All the adjacent cells of the path are 8-directionally connected (i.e., they are different and they share an edge or a corner).The length of a clear path is the number of visited cells of this path.
Example 1:
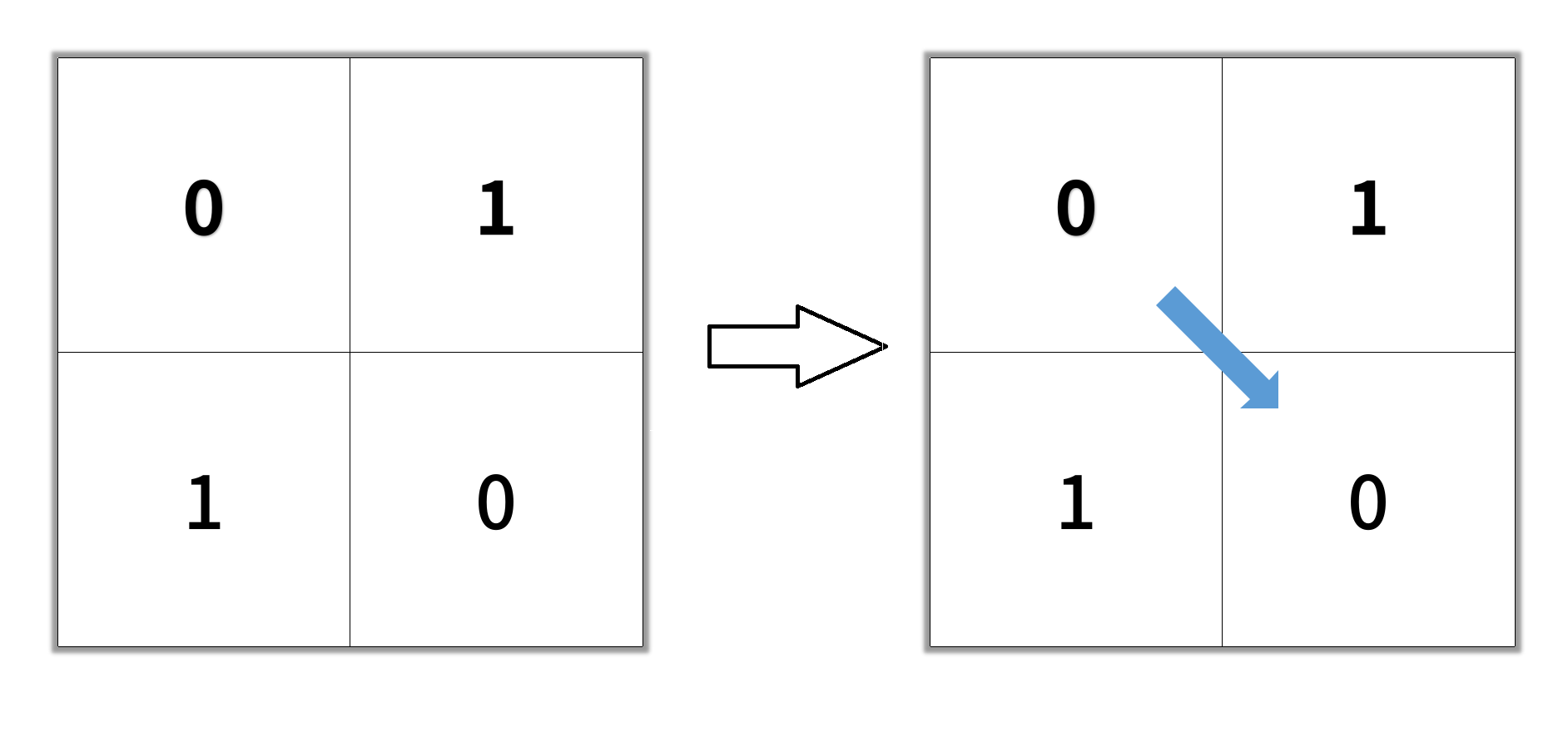
Input: grid = [[0,1],[1,0]] Output: 2
Example 2:
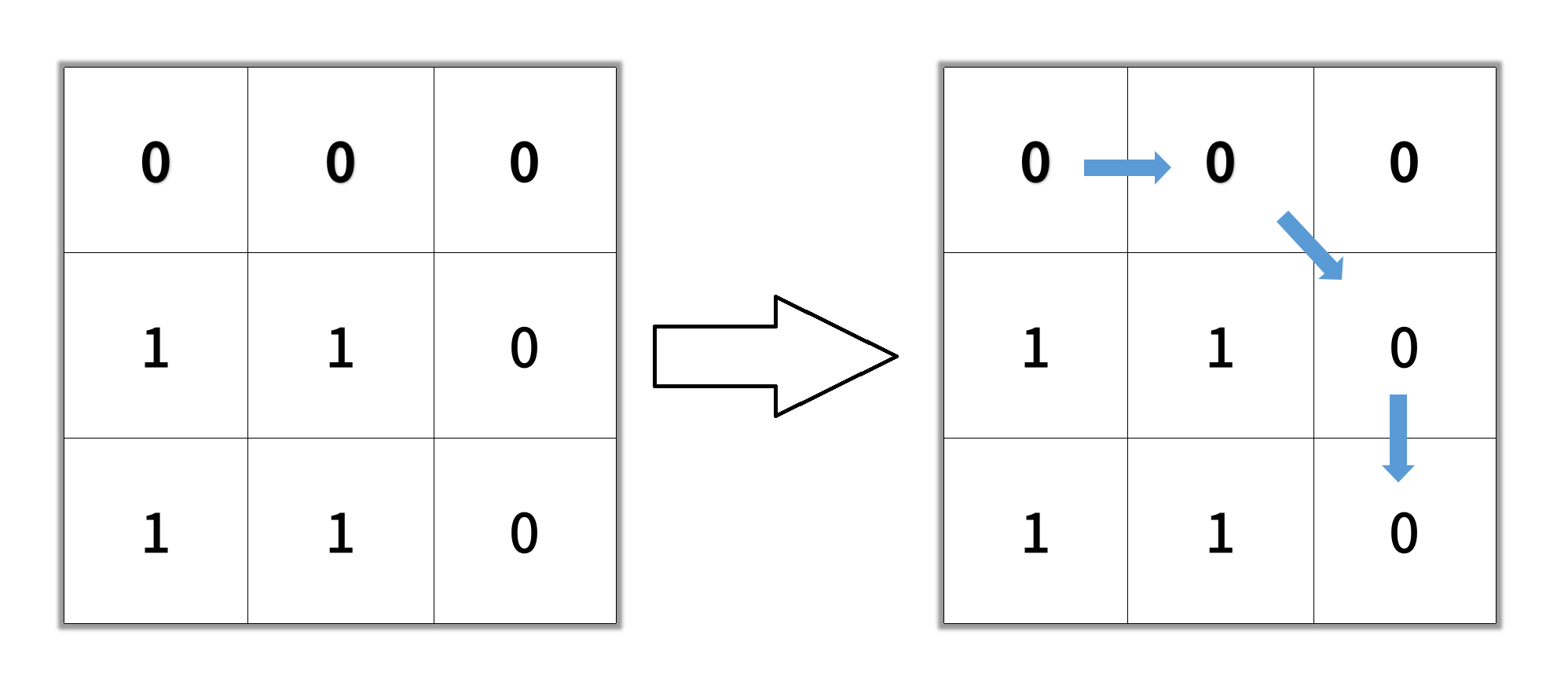
Input: grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]] Output: 4
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]] Output: -1
Constraints:
n == grid.length n == grid[i].length 1 <= n <= 100 grid[i][j] is 0 or 1
- code A star
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
max_row = len(grid) - 1
max_col = len(grid[0]) - 1
directions = [
(-1, -1), (-1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, -1), (0, 1), (1, -1), (1, 0), (1, 1)]
# Helper function to find the neighbors of a given cell.
def get_neighbours(row, col):
for row_difference, col_difference in directions:
new_row = row + row_difference
new_col = col + col_difference
if not(0 <= new_row <= max_row and 0 <= new_col <= max_col):
continue
if grid[new_row][new_col] != 0:
continue
yield (new_row, new_col)
# Helper function for the A* heuristic.
def best_case_estimate(row, col):
return max(max_row - row, max_col - col)
# Check that the first and last cells are open.
if grid[0][0] or grid[max_row][max_col]:
return -1
# Set up the A* search.
visited = set()
# Entries on the priority queue are of the form
# (total distance estimate, distance so far, (cell row, cell col))
priority_queue = [(1 + best_case_estimate(0, 0), 1, (0, 0))]
while priority_queue:
estimate, distance, cell = heapq.heappop(priority_queue)
if cell in visited: # Have we already found the best path to this cell?
continue
if cell == (max_row, max_col):
return distance
visited.add(cell)
for neighbour in get_neighbours(*cell):
# The check here isn't necessary for correctness, but it
# leads to a substantial performance gain.
if neighbour in visited:
continue
estimate = best_case_estimate(*neighbour) + distance + 1
entry = (estimate, distance + 1, neighbour)
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, entry)
# There was no path.
return -1
- code bfs
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if grid[0][0] == 1: return -1
n = len(grid)
def get_nei(i,j):
nei = []
directions = [(-1,0),(-1,1),(0,1),(1,1),(1,0),(1,-1),(0,-1),(-1,-1)]
for di, dj in directions:
next_i, next_j = di + i, dj + j
if 0 <= next_i < n and 0 <= next_j < n and grid[next_i][next_j] == 0:
nei.append((next_i, next_j))
return nei
step = 0
q = deque([(0,0)])
visited = set([(0,0)])
while q:
step += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
cur_i, cur_j = q.popleft()
if cur_i == cur_j == n - 1 : return step
for nei in get_nei(cur_i, cur_j):
if nei not in visited:
q.append(nei)
visited.add(nei)
return -1