BFS Template
/**
* Return the length of the shortest path between root and target node.
*/
int BFS(Node root, Node target) {
Queue<Node> queue; // store all nodes which are waiting to be processed
Set<Node> visited; // store all the nodes that we've visited
int step = 0; // number of steps neeeded from root to current node
// initialize
add root to queue;
add root to visited;
// BFS
while (queue is not empty) {
step = step + 1;
// iterate the nodes which are already in the queue
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Node cur = the first node in queue;
return step if cur is target;
for (Node next : the neighbors of cur) {
if (next is not in used) {
add next to queue;
add next to visited;
}
}
remove the first node from queue;
}
}
return -1; // there is no path from root to target
}
133. Clone graph
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph. Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph. Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors. class Node { public int val; public List neighbors; }
class Solution:
def cloneGraph(self, node): # BFS
if not node:
return node
m = {node: Node(node.val)}
deque = collections.deque([node])
while deque:
n = deque.popleft()
for neigh in n.neighbors:
if neigh not in m:
deque.append(neigh)
m[neigh] = Node(neigh.val)
m[n].neighbors.append(m[neigh])
return m[node]
- code bfs
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val,List<Node> _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
// Hash map to save the visited node and it's respective clone
// as key and value respectively. This helps to avoid cycles.
HashMap<Node, Node> visited = new HashMap();
// Put the first node in the queue
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node> ();
queue.add(node);
// Clone the node and put it in the visited dictionary.
visited.put(node, new Node(node.val, new ArrayList()));
// Start BFS traversal
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// Pop a node say "n" from the from the front of the queue.
Node n = queue.remove();
// Iterate through all the neighbors of the node "n"
for (Node neighbor: n.neighbors) {
if (!visited.containsKey(neighbor)) {
// Clone the neighbor and put in the visited, if not present already
visited.put(neighbor, new Node(neighbor.val, new ArrayList()));
// Add the newly encountered node to the queue.
queue.add(neighbor);
}
// Add the clone of the neighbor to the neighbors of the clone node "n".
visited.get(n).neighbors.add(visited.get(neighbor));
}
}
// Return the clone of the node from visited.
return visited.get(node);
}
}
752. open the lock
You have a lock in front of you with 4 circular wheels. Each wheel has 10 slots: ‘0’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘4’, ‘5’, ‘6’, ‘7’, ‘8’, ‘9’. The wheels can rotate freely and wrap around: for example we can turn ‘9’ to be ‘0’, or ‘0’ to be ‘9’. Each move consists of turning one wheel one slot. The lock initially starts at ‘0000’, a string representing the state of the 4 wheels. You are given a list of deadends dead ends, meaning if the lock displays any of these codes, the wheels of the lock will stop turning and you will be unable to open it. Given a target representing the value of the wheels that will unlock the lock, return the minimum total number of turns required to open the lock, or -1 if it is impossible.
Example 1: Input: deadends = [“0201”,“0101”,“0102”,“1212”,“2002”], target = “0202” Output: 6 Explanation: A sequence of valid moves would be “0000” -> “1000” -> “1100” -> “1200” -> “1201” -> “1202” -> “0202”. Note that a sequence like “0000” -> “0001” -> “0002” -> “0102” -> “0202” would be invalid, because the wheels of the lock become stuck after the display becomes the dead end “0102”.
Example 2: Input: deadends = [“8888”], target = “0009” Output: 1 Explanation: We can turn the last wheel in reverse to move from “0000” -> “0009”.
class Solution:
def openLock(self, deadends: List[str], target: str) -> int:
if "0000" in deadends:
return -1
queue = collections.deque()
queue.append(('0000', 0))
visited = set('0000')
visited.update(deadends)
while queue:
string, step = queue.popleft()
if string == target:
return step
for i in range(4):
num = int(string[i])
for dx in (-1, 1):
num_new = (num + dx) % 10
string_new = string[:i] + str(num_new) + string[i+1:]
if string_new not in visited:
queue.append((string_new, step+1))
visited.add(string_new)
return -1
class Solution:
def openLock(self, deadends: List[str], target: str) -> int:
if "0000" in deadends:
return -1
step = -1
q = collections.deque(["0000"])
visited = set("0000")
visited.update(deadends)
def findNeighbor(node):
neighbors = []
for i,v in enumerate(node):
if v == "0":
l, r = "9", "1"
elif v == "9":
l, r = "8", "0"
else:
l, r = str(int(v)-1), str(int(v)+1)
neighbors.append(node[:i] + l + node[i+1:])
neighbors.append(node[:i] + r + node[i+1:])
return neighbors
while q:
step += 1
cur_q_size = len(q)
while cur_q_size:
cur_q_size -= 1
cur = q.popleft()
if cur == target:
return step
neighbors = findNeighbor(cur)
for neighbor in neighbors:
if neighbor not in visited:
q.append(neighbor)
visited.add(neighbor)
return -1
- code
class Solution {
public int openLock(String[] deadends, String target) {
Set<String> dead = new HashSet();
for (String d: deadends) dead.add(d);
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList();
queue.offer("0000");
queue.offer(null);
Set<String> seen = new HashSet();
seen.add("0000");
int depth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String node = queue.poll();
if (node == null) {
depth++;
if (queue.peek() != null)
queue.offer(null);
} else if (node.equals(target)) {
return depth;
} else if (!dead.contains(node)) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
for (int d = -1; d <= 1; d += 2) {
int y = ((node.charAt(i) - '0') + d + 10) % 10;
String nei = node.substring(0, i) + ("" + y) + node.substring(i+1);
if (!seen.contains(nei)) {
seen.add(nei);
queue.offer(nei);
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
279. Perfect squares
Given an integer n, return the least number of perfect square numbers that sum to n. A perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 1, 4, 9, and 16 are perfect squares while 3 and 11 are not.
Example 1: Input: n = 12 Output: 3 Explanation: 12 = 4 + 4 + 4.
Example 2: Input: n = 13 Output: 2 Explanation: 13 = 4 + 9.
class Solution(object):
def numSquares(self, n):
candidates = collections.deque([0])
visited = set()
potential = [i*i for i in range(1, int(n**0.5) + 1)]
step = 0
while candidates:
step += 1
sz = len(candidates)
for _ in range(sz):
cur = candidates.popleft()
for v in potential:
if v + cur < n and v + cur not in visited:
candidates.append(v + cur)
visited.add(v + cur)
elif v + cur == n:
return step
- code bfs
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
ArrayList<Integer> square_nums = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 1; i * i <= n; ++i) {
square_nums.add(i * i);
}
Set<Integer> queue = new HashSet<Integer>();
queue.add(n);
int level = 0;
while (queue.size() > 0) {
level += 1;
Set<Integer> next_queue = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (Integer remainder : queue) {
for (Integer square : square_nums) {
if (remainder.equals(square)) {
return level;
} else if (remainder < square) {
break;
} else {
next_queue.add(remainder - square);
}
}
}
queue = next_queue;
}
return level;
}
}
733. Flood fill
CompaniesAn image is represented by an m x n integer grid image where image[i][j] represents the pixel value of the image.
You are also given three integers sr, sc, and newColor. You should perform a flood fill on the image starting from the pixel image[sr][sc].
To perform a flood fill, consider the starting pixel, plus any pixels connected 4-directionally to the starting pixel of the same color as the starting pixel, plus any pixels connected 4-directionally to those pixels (also with the same color), and so on. Replace the color of all of the aforementioned pixels with newColor. Return the modified image after performing the flood fill.
class Solution:
def floodFill(self, image, sr, sc, newColor):
old, m, n = image[sr][sc], len(image), len(image[0])
if old != newColor:
q = collections.deque([(sr, sc)])
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
image[i][j] = newColor
for x, y in ((i - 1, j), (i + 1, j), (i, j - 1), (i, j + 1)):
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and image[x][y] == old:
q.append((x, y))
return image
You are given coins of different denominations and a total amount of money amount. Write a function to compute the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1. You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
Example 1: Input: coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11 Output: 3 Explanation: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1
Example 2: Input: coins = [2], amount = 3Output: -1
class Solution:
def coinChange(self, coins: List[int], amount: int) -> int:
if amount == 0: return 0
visited = set()
potential = collections.deque(coins)
visited.update(coins)
step = 0
while potential:
step += 1
for _ in range(len(potential)):
if potential[0] == amount:
return step
for c in coins:
if c + potential[0] not in visited:
potential.append(c + potential[0])
visited.add(c + potential[0])
potential.popleft()
if all(p > amount for p in potential):
break
return -1
class Solution:
def coinChange(self, coins: List[int], amount: int) -> int:
if amount == 0: return 0
queue = [[0, 0]]
visited = {0}
step = 0
for node, step in queue:
for coin in coins:
if node + coin == amount: return step + 1
elif node + coin < amount and node + coin not in visited:
queue.append([node + coin, step + 1])
visited.add(node + coin)
return -1
542. 01-matrix
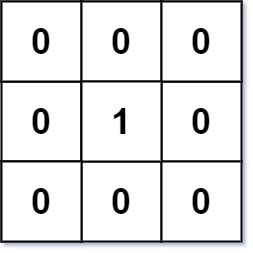
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell. The distance between two adjacent cells is 1.
Example 1:
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]] Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
class Solution:
def updateMatrix(self, matrix):
rows_len, cols_len = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
start_0 = [(x,y) for x in range(rows_len) for y in range(cols_len) if matrix[x][y] == 0]
visited = set()
q = deque(start_0)
visited.update(start_0)
# result = [[-1 for _ in range(cols_len)] for y in range(rows_len)]
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
x, y = q.popleft()
for d in [[0,1],[0,-1],[1,0],[-1,0]]:
m, n = x + d[0], y + d[1]
if 0 <= m < rows_len and 0 <= n < cols_len and (m,n) not in visited:
matrix[m][n] = matrix[x][y] + 1 # update matrix directly
q.append((m, n))
visited.add((m, n))
return matrix
127. Word ladder
A transformation sequence from word beginWord to word endWord using a dictionary wordList is a sequence of words beginWord -> s1 -> s2 -> … -> sk such that:
Every adjacent pair of words differs by a single letter. Every si for 1 <= i <= k is in wordList. Note that beginWord does not need to be in wordList. sk == endWordGiven two words, beginWord and endWord, and a dictionary wordList, return the number of words in the shortest transformation sequence from beginWord to endWord__, or __0__ if no such sequence exists.__
**Example 1:**
Input: beginWord = “hit”, endWord = “cog”, wordList = [“hot”,“dot”,“dog”,“lot”,“log”,“cog”] Output: 5 Explanation: One shortest transformation sequence is “hit” -> “hot” -> “dot” -> “dog” -> cog", which is 5 words long.
class Solution(object):
def ladderLength(self, beginWord, endWord, wordList):
def construct_dict(word_list):
d = {}
for word in word_list:
for i in range(len(word)):
s = word[:i] + "_" + word[i+1:]
d[s] = d.get(s, []) + [word]
return d
def bfs_words(begin, end, dict_words):
queue, visited = deque([(begin, 1)]), set()
while queue:
word, steps = queue.popleft()
if word not in visited:
visited.add(word)
if word == end:
return steps
for i in range(len(word)):
s = word[:i] + "_" + word[i+1:]
neigh_words = dict_words.get(s, [])
for neigh in neigh_words:
if neigh not in visited:
queue.append((neigh, steps + 1))
return 0
d = construct_dict(set(wordList))
return bfs_words(beginWord, endWord, d)
- code
class Solution {
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
// Since all words are of same length.
int L = beginWord.length();
// Dictionary to hold combination of words that can be formed,
// from any given word. By changing one letter at a time.
Map<String, List<String>> allComboDict = new HashMap<>();
wordList.forEach( word -> {
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
// Key is the generic word
// Value is a list of words which have the same intermediate generic word.
String newWord = word.substring(0, i) + '*' + word.substring(i + 1, L);
List<String> transformations = allComboDict.getOrDefault(newWord, new ArrayList<>());
transformations.add(word);
allComboDict.put(newWord, transformations);
}
});
// Queue for BFS
Queue<Pair<String, Integer>> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.add(new Pair(beginWord, 1));
// Visited to make sure we don't repeat processing same word.
Map<String, Boolean> visited = new HashMap<>();
visited.put(beginWord, true);
while (!Q.isEmpty()) {
Pair<String, Integer> node = Q.remove();
String word = node.getKey();
int level = node.getValue();
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
// Intermediate words for current word
String newWord = word.substring(0, i) + '*' + word.substring(i + 1, L);
// Next states are all the words which share the same intermediate state.
for (String adjacentWord : allComboDict.getOrDefault(newWord, new ArrayList<>())) {
// If at any point if we find what we are looking for
// i.e. the end word - we can return with the answer.
if (adjacentWord.equals(endWord)) {
return level + 1;
}
// Otherwise, add it to the BFS Queue. Also mark it visited
if (!visited.containsKey(adjacentWord)) {
visited.put(adjacentWord, true);
Q.add(new Pair(adjacentWord, level + 1));
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix
Given an n x n binary matrix grid, return the length of the shortest clear path in the matrix. If there is no clear path, return -1. A clear path in a binary matrix is a path from the top-left cell (i.e., (0, 0)) to the bottom-right cell (i.e., (n - 1, n - 1)) such that:
All the visited cells of the path are 0. All the adjacent cells of the path are 8-directionally connected (i.e., they are different and they share an edge or a corner).The length of a clear path is the number of visited cells of this path.
Example 1:
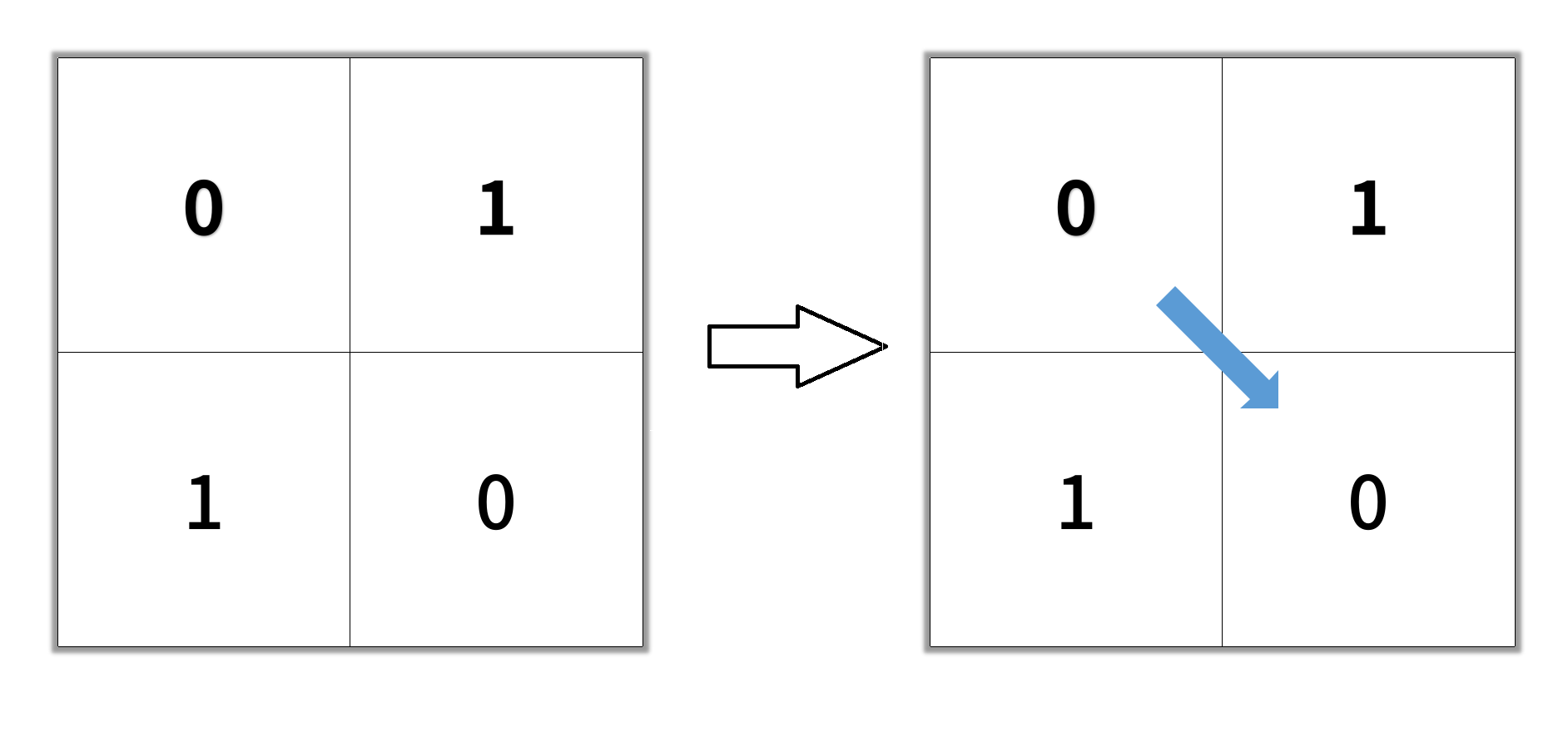
Input: grid = [[0,1],[1,0]] Output: 2
Example 2:
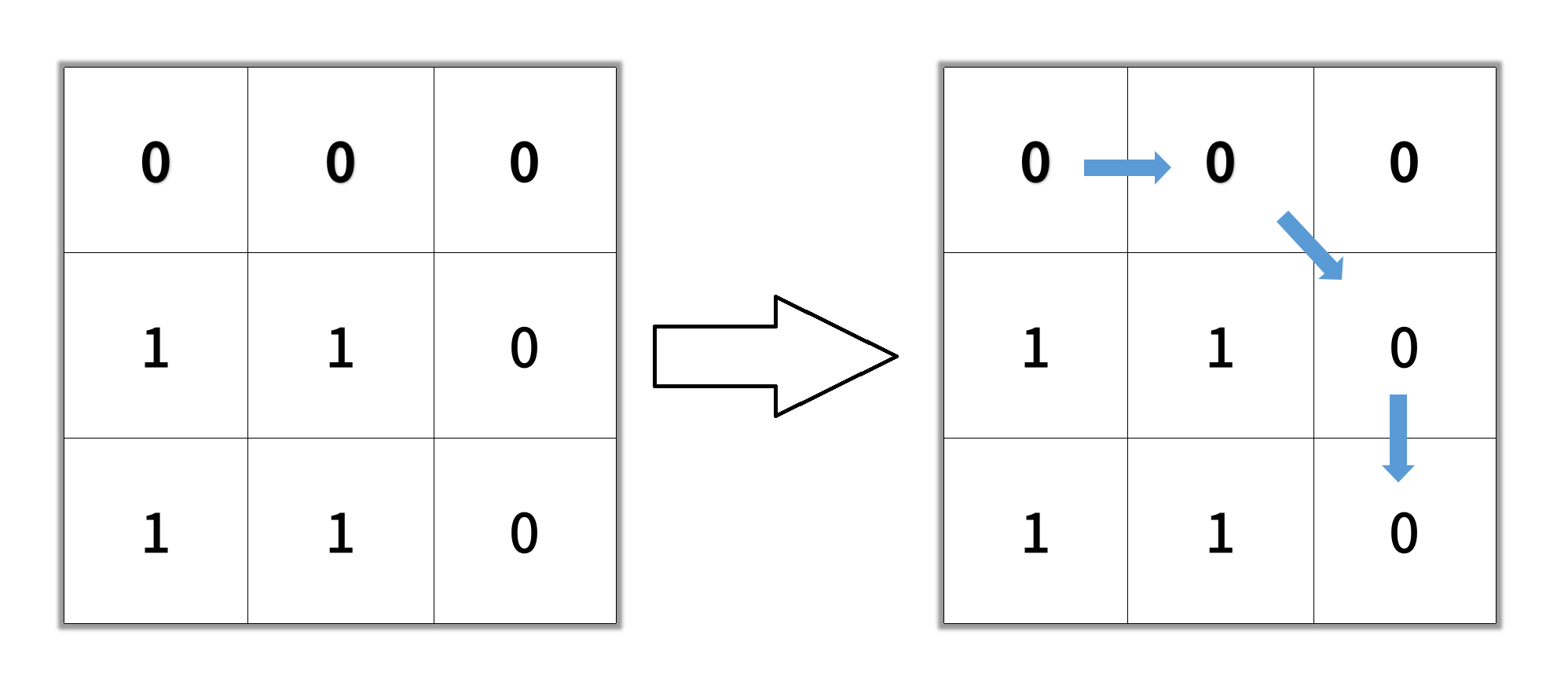
Input: grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]] Output: 4
- code #astar
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
max_row = len(grid) - 1
max_col = len(grid[0]) - 1
directions = [
(-1, -1), (-1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, -1), (0, 1), (1, -1), (1, 0), (1, 1)]
# Helper function to find the neighbors of a given cell.
def get_neighbours(row, col):
for row_difference, col_difference in directions:
new_row = row + row_difference
new_col = col + col_difference
if not(0 <= new_row <= max_row and 0 <= new_col <= max_col):
continue
if grid[new_row][new_col] != 0:
continue
yield (new_row, new_col)
# Helper function for the A* heuristic.
def best_case_estimate(row, col):
return max(max_row - row, max_col - col)
# Check that the first and last cells are open.
if grid[0][0] or grid[max_row][max_col]:
return -1
# Set up the A* search.
visited = set()
# Entries on the priority queue are of the form
# (total distance estimate, distance so far, (cell row, cell col))
priority_queue = [(1 + best_case_estimate(0, 0), 1, (0, 0))]
while priority_queue:
estimate, distance, cell = heapq.heappop(priority_queue)
if cell in visited: # Have we already found the best path to this cell?
continue
if cell == (max_row, max_col):
return distance
visited.add(cell)
for neighbour in get_neighbours(*cell):
# The check here isn't necessary for correctness, but it
# leads to a substantial performance gain.
if neighbour in visited:
continue
estimate = best_case_estimate(*neighbour) + distance + 1
entry = (estimate, distance + 1, neighbour)
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, entry)
# There was no path.
return -1
- code bfs
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if grid[0][0] == 1: return -1
n = len(grid)
def get_nei(i,j):
nei = []
directions = [(-1,0),(-1,1),(0,1),(1,1),(1,0),(1,-1),(0,-1),(-1,-1)]
for di, dj in directions:
next_i, next_j = di + i, dj + j
if 0 <= next_i < n and 0 <= next_j < n and grid[next_i][next_j] == 0:
nei.append((next_i, next_j))
return nei
step = 0
q = deque([(0,0)])
visited = set([(0,0)])
while q:
step += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
cur_i, cur_j = q.popleft()
if cur_i == cur_j == n - 1 : return step
for nei in get_nei(cur_i, cur_j):
if nei not in visited:
q.append(nei)
visited.add(nei)
return -1
class Solution {
private static final int[][] directions =
new int[][]{{-1, -1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 0}, {1, 1}};
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {
// Firstly, we need to check that the start and target cells are open.
if (grid[0][0] != 0 || grid[grid.length - 1][grid[0].length - 1] != 0) {
return -1;
}
// Set up the BFS.
Queue<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
grid[0][0] = 1;
queue.add(new int[]{0, 0});
// Carry out the BFS
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = queue.remove();
int row = cell[0];
int col = cell[1];
int distance = grid[row][col];
if (row == grid.length - 1 && col == grid[0].length - 1) {
return distance;
}
for (int[] neighbour : getNeighbours(row, col, grid)) {
int neighbourRow = neighbour[0];
int neighbourCol = neighbour[1];
queue.add(new int[]{neighbourRow, neighbourCol});
grid[neighbourRow][neighbourCol] = distance + 1;
}
}
// The target was unreachable.
return -1;
}
private List<int[]> getNeighbours(int row, int col, int[][] grid) {
List<int[]> neighbours = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < directions.length; i++) {
int newRow = row + directions[i][0];
int newCol = col + directions[i][1];
if (newRow < 0 || newCol < 0 || newRow >= grid.length
|| newCol >= grid[0].length
|| grid[newRow][newCol] != 0) {
continue;
}
neighbours.add(new int[]{newRow, newCol});
}
return neighbours;
}
}